In terms of risk management, you often hear about inherent risk, residual risk, inherent risk, intrinsic risk, or residual risk. But what are they really? What is the difference between these terms? Why assess them?
Discover the answers to these questions here!

Inherent Risk vs Residual Risk
Why assess inherent risk and residual risk?
By evaluating risks in these two scenarios, inherent and residual, you will highlight the significance of certain risks and the essential control measures. In short, you will better manage your risks.
Let’s find out how!
What is ‘inherent risk’?
Inherent risk corresponds to the evaluation of risk without any control measures in place. Depending on the sector, it is also referred to as inherent risk or intrinsic risk to the company’s activities.
Take, for example, the ‘Risk of error in payroll processing’. If the company does not implement any control measures, one can imagine the risk occurring. Inattention by an employee; omission to include expenses, bonuses, changes in taxation; fraud; significant amounts being released without alert; inability to detect errors…
The inherent risk assessment could be as follows:

This risk will vary in magnitude depending on the establishment. Let’s consider the case of two companies. One has 100 employees based solely in France, and the other has 100 employees spread across several countries with different laws. The inherent risk assessment will not be the same.
Another example is the ‘Risk of fire in the premises’.
Imagine a company where there is no prevention, no safety measures, and no controls. Imagine that there are no fire alarms, no firefighting equipment, and no business continuity plan. The inherent risk assessment could be as follows:

Again, the inherent risk will not be the same for all companies. An industry that stores hazardous products will likely assess this risk as severe, unlike a service company that only has an office with a few computers.
What is a ‘Control Measure’?
Control measures are the methods implemented to reduce the likelihood of a risk occurring and/or its impact if it does occur. These measures can include control actions, procedures, physical means, etc.
Here are examples of control measures that could be implemented for the two risks previously discussed.

What is ‘residual risk’?
Residual risk refers to the risk assessment considering the control measures implemented by the company.
In the examples below, the control measures have helped to reduce the risks.
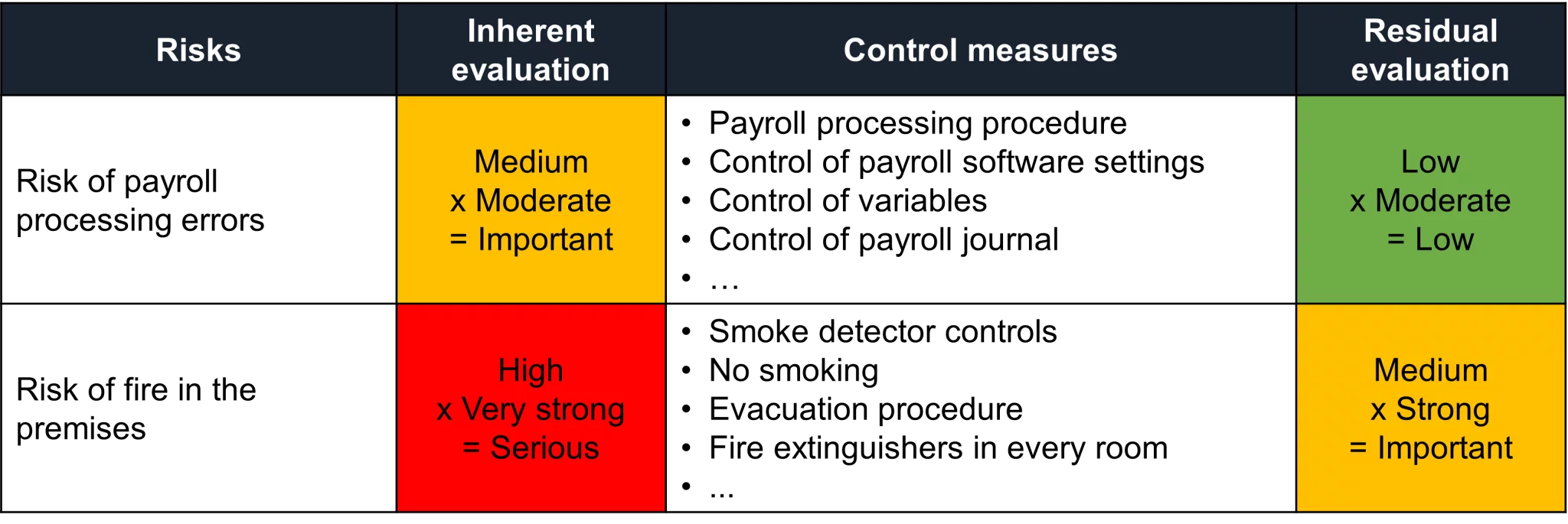
Thanks to the measures implemented, the level of the ‘Risk of payroll processing errors’ has changed from significant to low, and the level of the ‘Risk of fire in the premises’ from severe to low.
What are the advantages of assessing ‘inherent risk’?
Highlighting the significance of certain risks
Let’s revisit the example above. By assessing only the residual risk, a company would consider the ‘Risk of fire in the premises’ as important as the ‘Risk of payroll processing errors’ since both are low. However, with the assessment of inherent risk, we clearly see the true significance of the fire risk.
Identifying essential control measures
Assessing inherent risk also highlights the importance of certain control measures and shows that it is essential to verify their effectiveness properly. If a company evaluated only the residual risk, it might reduce control measures in case of insufficient resources, for example, or it might be more lax in monitoring controls. Whereas, with the view of inherent risk, the importance of control measures is emphasized.
Ensuring a common view of risks
Another advantage of assessing inherent risk is that it provides a common vision among employees. Ask two colleagues to evaluate the ‘Risk of payroll processing errors’ in your company. One will tell you it is low because they are considering all the measures in place, and the other will respond that it is significant because they think in terms of ‘residual risk’.
In summary, assessing both inherent and residual risks allows you to better manage your risks!
Don’t forget, to ensure the effectiveness of your risk management, it is important to reassess risks each year and to monitor the performance of control measures, adjusting them if necessary. A risk management software like Optimiso Suite is an ideal tool to ensure good tracking of risks and controls.
Finally, it is always good to remember that a company without risk does not exist. It is good to live with risks as long as they are known and controlled.
