A QSE system (Quality, Safety, Environment) is an integrated approach that combines three key aspects: product or service quality, employee safety, and environmental protection.
Are you considering implementing a QSE system in your company?
Good news—Optimiso Group is here to share its proven methodology, successfully applied with numerous clients.

Benefits of a QSE system
Implementing a QSE system in your company offers numerous advantages:
- Continuous improvement: regular evaluation and optimization of operational processes drive ongoing enhancements.
- Enhanced risk management: better control over risks related to product quality, safety, and environmental impact.
- Regulatory compliance: ensures adherence to legal requirements, helping you avoid penalties and build trust with stakeholders.
- Economic growth: reassures prospects with the implemented measures, opening doors to new markets.
QSE system or integrated management system?
Quality, Safety, and Environment (QSE) initiatives share several key components, such as activity identification, improvement management, and internal audits.
To avoid redundancies and simplify documentation, it’s recommended to adopt an integrated management approach for QSE. This method offers several advantages:
- Reduced Documentation Volume: Minimize repetitive paperwork.
- Vocabulary Harmonization: Ensure consistent terminology across processes.
- Documentation Standardization: Streamline and unify formats.
- Cost Optimization: Lower management expenses.
- Audit Cost Reduction: Cut costs associated with internal and external audits.
Many companies now adopt QSE software to streamline these processes. Optimiso Suite provides centralized management for processes, procedures, incidents, and more.
Interested in learning more? Watch our presentation video or book a personalized demo. Join the many businesses turning QSE challenges into tangible benefits!
Standards for a QSE system
Three ISO certifications address the requirements of a QSE system:
- ISO 9001 for Quality
- ISO 14001 for environment
- ISO 45001 for Safety
Steps to implement a QSE system
Implementing a QSE system is a comprehensive management project that may span several months and requires ongoing maintenance. To ensure its success, applying the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is highly recommended.
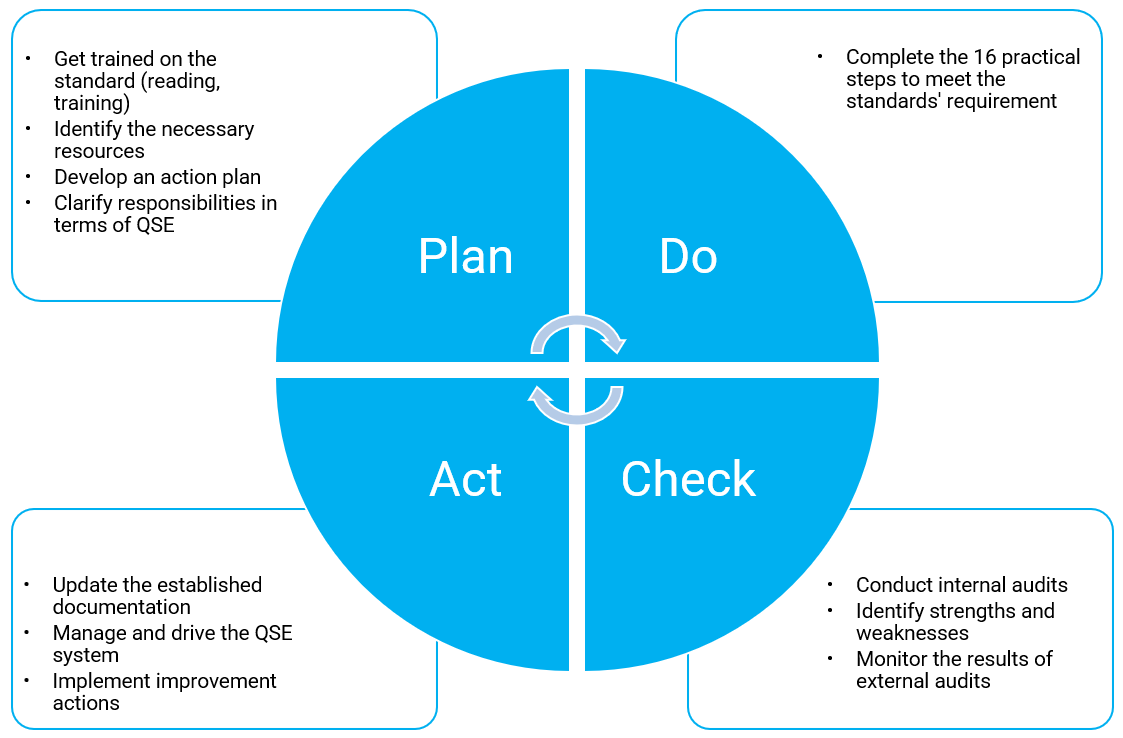
1. Presenting the project to employees
Engaging employees from the very beginning is essential to ensure their commitment to the QSE initiative. A presentation (preferably in person) should include the following key points:
- Objectives of the QSE Initiative
- Introduction to ISO Standards: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001
- Benefits for Employees and the Company
- Project Steps and Timeline:
- Employee Involvement
- Support from Leadership
2. Context and scope description
In a QSE system, defining the context should not be viewed as merely a regulatory requirement or a formality to satisfy auditors. It serves as a cornerstone for strategic decision-making by leadership. Key elements to emphasize include:
- External factors : Use the PESTEL model to analyze Political, Economic, Social, Environmental, Technological, and Legal influences. Complement this with a SWOT analysis to identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- Internal factors : Consider the company’s culture, values, and operational structure.
- Stakeholders : Identify and address the needs of clients, unions, pressure groups, private or public shareholders, authorities, and others.
Establishing the scope of the QSE system at the outset is crucial for focusing efforts and resources effectively. For instance, in an industrial company, determine whether the system will encompass all activities or target specific areas like production, administrative functions, or a particular geographic site.
By clearly defining these elements, your QSE system will be well-positioned to drive strategic alignment and operational success.
3. Implementation of legal monitoring
Legal monitoring is an essential pillar of a QSE management system. It enables companies to manage the various regulatory constraints they face. This approach requires responsiveness to changes as well as the ability to prove the actions taken to address them.
The Optimiso Suite software offers an effective solution for legal monitoring. You can record each regulatory requirement and, for each relevant section, specify the measures implemented.
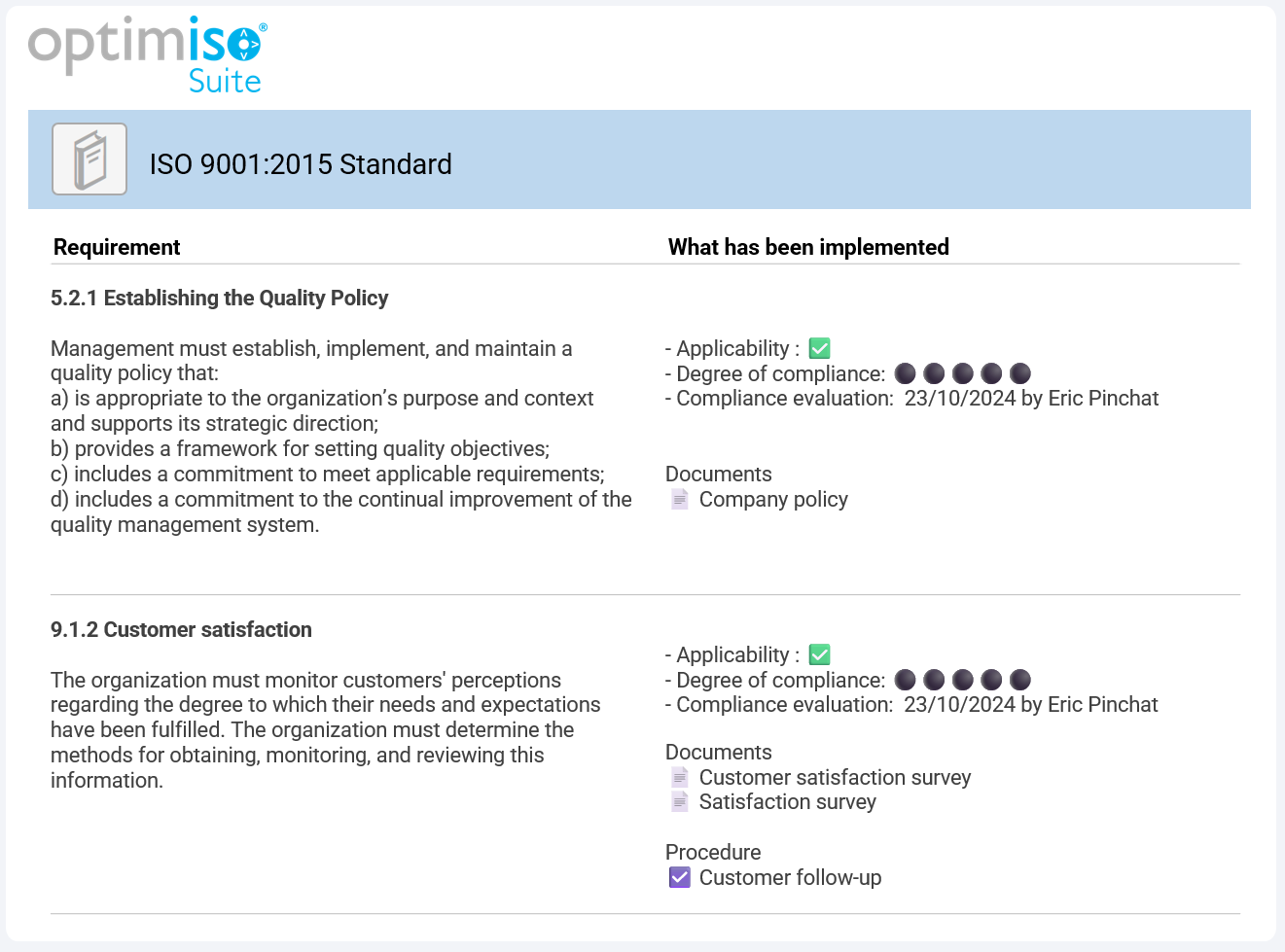
4. Inventory and description of activities
At this stage, the goal is to answer the question, “What do we do in the company?” To achieve this, you will list the activities (or processes) performed.
Processes
The inventory of processes is often structured across multiple levels to facilitate understanding. For example, the “Human Resources” process could be organized as follows:

To delve deeper, detailed process sheets may include key elements such as:
- Steps of the process
- Associated risks
- Performance indicators
- Required resources
- Stakeholders
Process map
After the inventory, the process map provides an overview of the company’s activities, clarifying the interactions between different processes.
Procedures
It is recommended to describe key or complex activities in a simple and effective way for employees. These descriptions can take the form of procedures, operating methods, videos, and more.
5. Identification of risks and opportunities
At this stage, it is essential to identify risks and opportunities, including their impacts on Quality, Safety, and the Environment. While optional, risk assessment provides a clearer perspective.
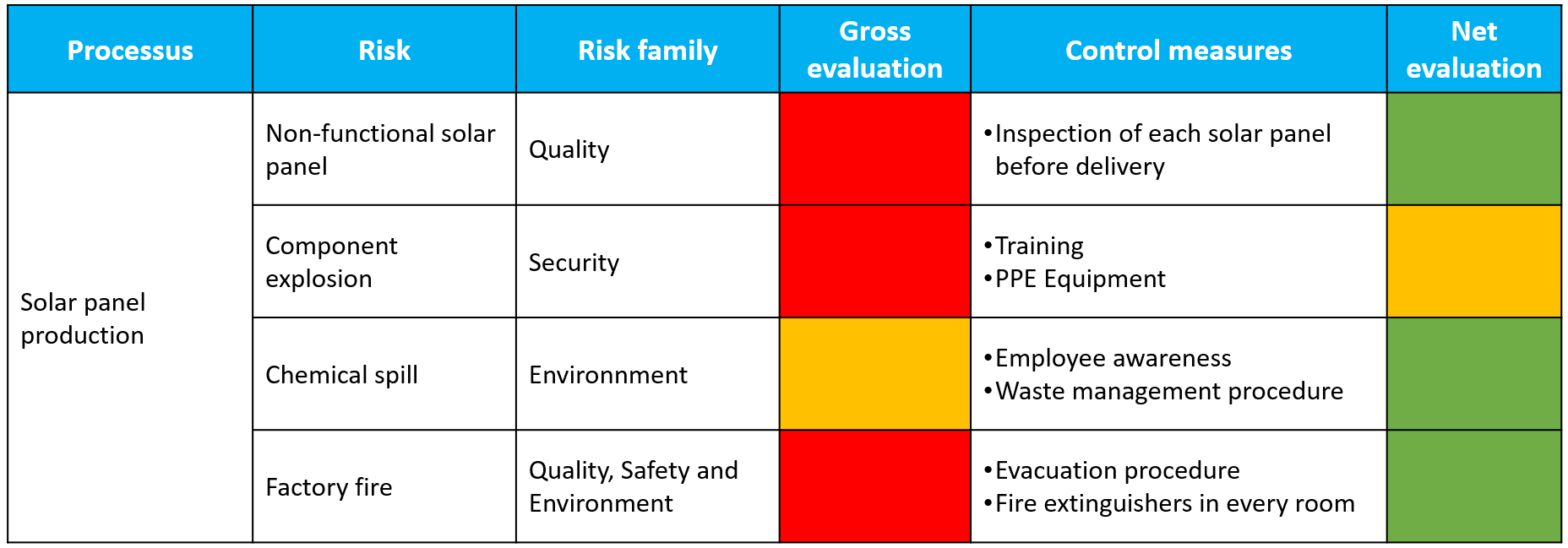
In terms of safety, the standards require the development of action plans to respond effectively to major incidents.
To explore this topic in more detail, check out this article: How to implement an effective business continuity plan?
6. Management of non-conformities and improvements
One of the primary objectives of a QSE system is to collect non-conformities to ensure that undesirable events do not recur. Similarly, managing improvements is crucial to ensuring continuous progress.
Providing a procedure for incident and improvement management will support business teams, who are often less familiar with QSE practices. This will encourage the proactive reporting of incidents and suggested improvements.
7. Identification of knowledge and skills
As with most ISO certifications, it is essential to assess employees’ skills and map their knowledge. This approach ensures the proper application of processes.
8. Supplier evaluation
Supplier evaluation is required by ISO 9001 certification. In a QSE (Quality, Safety, Environment) approach, you can also include criteria related to health/safety and the environment. The goal is to identify key suppliers who have a direct impact on the products or services you offer.
For each supplier, define specific criteria, establish a regular evaluation frequency, and determine whether an audit is necessary.
9. Customer satisfaction evaluation
The ISO 9001 standard requires regular evaluation of customer satisfaction to measure the effectiveness of the quality management system. There are many methods available to assess customer satisfaction.
10. QSE policy
The QSE policy is a document that formalizes the following:
- Management Commitment
- Company Purpose
- Commitment to Customer Satisfaction, Employee Safety, and Environmental Protection
- Commitment to Continuous Improvement
This policy must be communicated to employees and all relevant stakeholders.
11. Client and partner property
The ISO 9001 standard requires companies to identify and properly manage assets entrusted to them by clients or external partners. These assets may include materials, components, tools, equipment, premises, intellectual property, or personal data.
For example, in a real estate agency, the company manages the rental of buildings or apartments owned by the client. In such cases, it is important for the agency to identify these assets and describe their condition to ensure their protection and preservation.
12. Employee awareness of QSE
Training and informing employees play a key role in implementing the QSE system. Information sessions should be held regularly for current employees and during the onboarding of new team members. These sessions should cover the following topics:
- Progress of the QSE project
- Presentation of the QSE policy
- Management of reference documentation
- Internal audits
- Certification audits
For safety specifically, ISO 45001 requires going beyond basic awareness. Employees must actively participate in the initiatives. Here is a diagram that highlights the major activities involved.
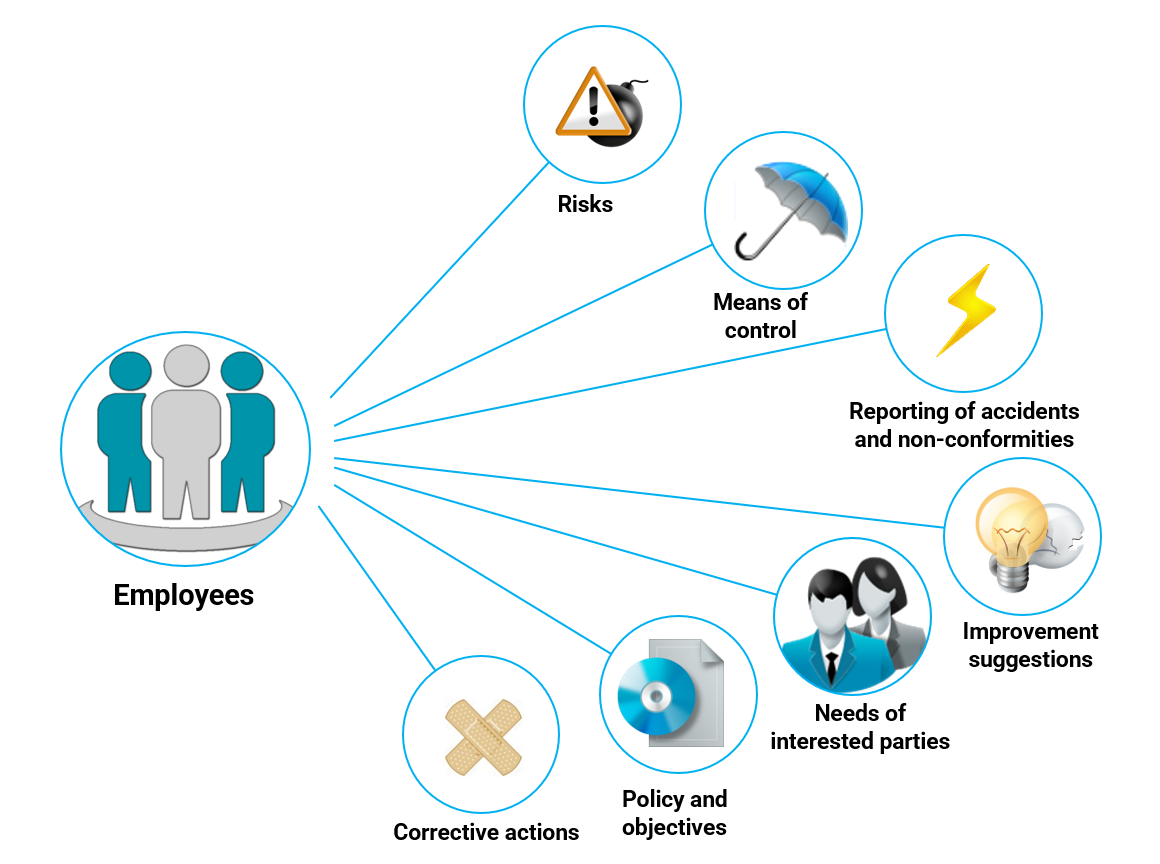
13. Management Review
During the implementation of the QSE system, it is recommended to schedule an initial management review halfway through to evaluate the actions undertaken and define objectives for the next steps. Subsequently, an annual review is recommended, covering the following points:
- Review QSE objectives
- Changes or adjustments to internal and external factors
- Monitoring of indicators, non-conformities, improvement actions, internal audits, resources allocated to QSE, etc.
- Opportunities for improvement
14. Internal audits
The internal audit ensures consistency between work practices and defined standards. It starts with training auditors and creating an audit plan.
In a QSE system, it is important to distinguish field activities from office activities. Auditors generally intervene at the end of the project, evaluating activities, collecting improvement suggestions, and identifying any incidents.
The results are then analyzed and presented to management, which implements the necessary corrective actions.
It is crucial to keep these audit reports as they will serve as evidence during the certification audit.
15. ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001 certification audits
It’s the big day! After all the hard work, the project finally materializes. The certification audits take place in two main phases:
Phase 1: Pre-certification audit
The auditor meets with the QSE manager and top management.
Objective: Ensure that all necessary documentation is in place and that the company complies with the requirements of ISO 9001, 45001, and 14001 standards.
Outcome: The auditor grants approval to proceed to the next phase and provides an audit plan.
Phase 2: Certification audit
After sharing the audit plan, the auditor interviews the QSE manager, top management, and a few employees to verify the following:
- Management’s commitment
- Compliance with ISO 9001, 14001, and 45001 requirements
- Proper functioning of continuous improvement
- Implementation of a risk-based approach
- Employee involvement in the QSE
At the end of the audit, the auditor gives an oral statement on the certification decision and highlights any discrepancies identified.
ISO 9001, 45001, and 14001 certifications follow a three-year cycle. After the initial certification audit, surveillance audits are conducted annually (years 1 and 2). At the end of the three-year cycle, a renewal audit is performed.
16. Daily management of the IMS
Congratulations! You now hold the triple ISO 9001, 45001, and 14001 certification. This marks the beginning of a new journey where you will maintain and improve your QSE system. You will need to regularly:
- Monitor certifications with the certification body
- Keep documentation up-to-date and accessible
- Reassess risks
- Track performance indicators
- Conduct internal audits
- Reevaluate employee competencies
- Reevaluate suppliers
- Ensure customer satisfaction, employee safety, and environmental protection
- Address incidents and non-conformities
- Follow up on improvement projects
- Communicate QSE initiatives internally and externally
- Organize a management review at least once a year
A QSE software solution can greatly simplify your daily management by centralizing the three systems in a single platform. With Optimiso Suite, all QSE-related elements (processes, procedures, documents, indicators, etc.) are accessible with just a few clicks. You save time before, during, and after audits.
Want to learn how? Watch this 2-minute presentation video or book a personalized demo.
These 16 steps structure the implementation of a QSE (Quality, Safety, and Environment) system and the achievement of ISO 9001, 45001, and 14001 certifications. They should help you fully leverage a QSE system that benefits both employees and management.
