What do the fortifications of Carcassonne and Internal Control have in common? They both involve lines of defense that serve to protect the castle on one hand, and to reduce and manage risks on the other.
In the context of governance, internal control, and risk management, the Three Lines of Defense Model is often discussed.
This concept, initiated by the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA), primarily aims to reduce risks associated with errors and fraud in businesses.
What exactly does it entail? What is the role of each line of defense? Discover this through concrete examples encountered in the field.

The Role of the Three Lines of Defense
The “warrior” origin of the term line of defense perfectly illustrates its role against adverse events and risks. Their occurrence can be reduced if the organization is well-defined and each line performs its role effectively.
The first line of defense represents risk management and controls handled by operational staff. These first-level controls are essential because they are directly related to the delivery of products or services to customers.
The second line of defense represents risk management and controls performed by support functions such as the Head of Internal Control, the Risk Manager, or the Compliance Officer. They initiate the controls and ensure their proper execution by the first line.
The third line of defense is the company’s internal audit, which is responsible for the administration of controls and, more broadly, the management of the risk control process.
The first two lines are directly driven by the Executive Management, which initiates the strategy and sets objectives. Regularly, these two lines must report to the Management the results of the controls and actions implemented. The third line of defense, meanwhile, is more independent and provides assurance and advice to the Executive Management and the Board of Directors.

Here are two concrete examples to illustrate the Three Lines of Defense Model.
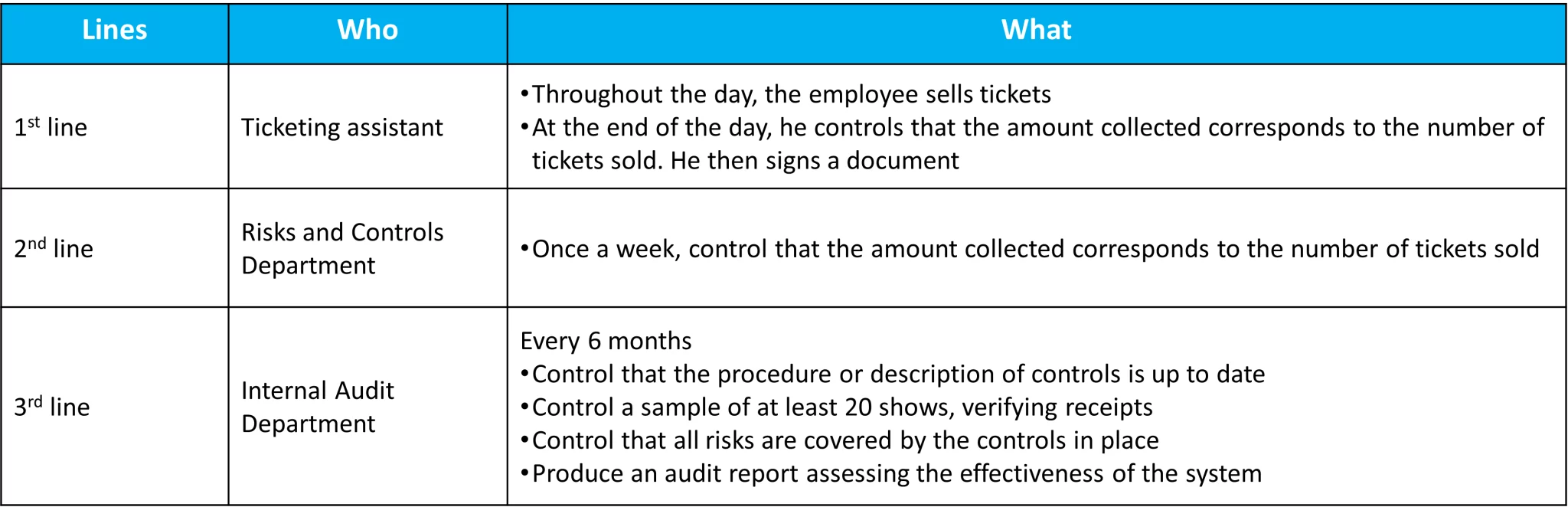
The Three Lines of Defense Model, example in a show ticket office
Let’s consider an example that everyone can understand: a show ticket office where there might be risks of errors or fraud. Controls can be implemented at multiple levels to manage these risks.
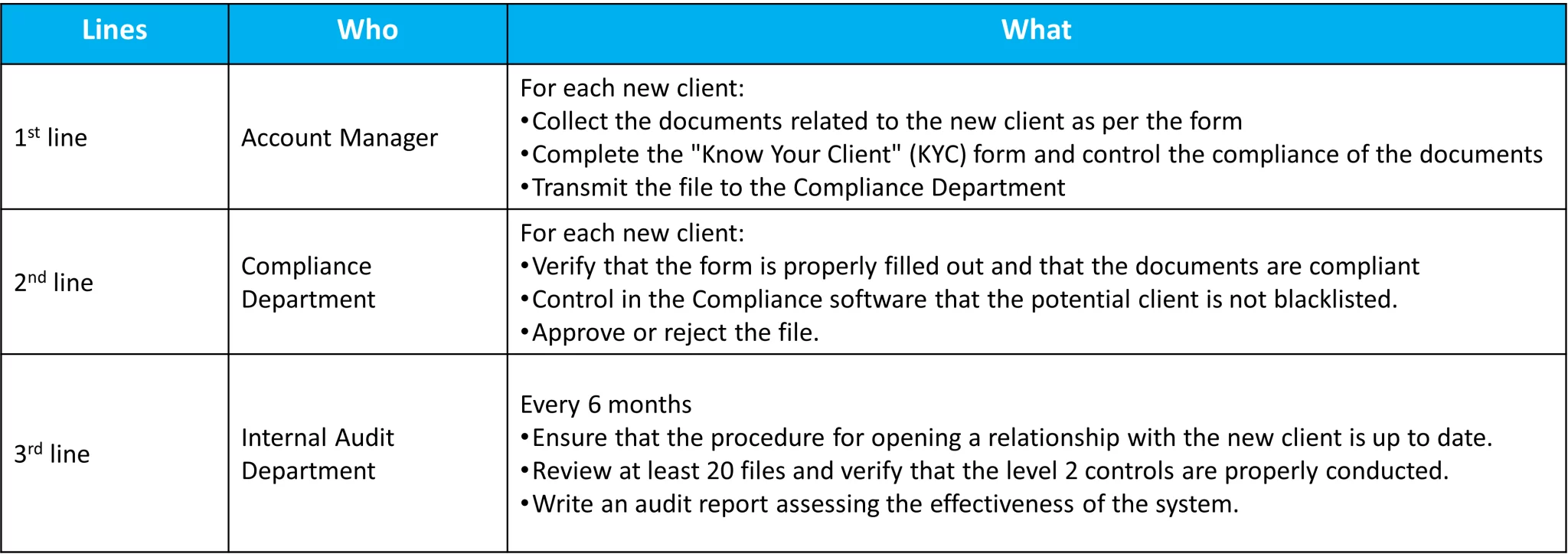
The Three Lines of Defense Model, example in a bank
The Three Lines Model is very prevalent in the banking sector. For example, when creating new customer accounts, banks must conduct checks to ensure that the potential customer does not pose a risk to them.
Here is a concrete illustration of what the three lines of defense might look like in this activity.
Continuous and periodic control
The concepts of continuous control and periodic control are sometimes associated with the Lines of Defense. Is there a link between these two concepts?
Continuous control covers the daily checks carried out by operational staff in the context of processing transactions (first level) and by internal control, risk management, and compliance (second level).
Periodic control allows for a certain perspective and encompasses the third-level controls conducted by internal audit (third level).

Are there other lines of defense?
Depending on the industry, it is possible to find additional lines of defense. This may be related to the prevailing regulations or simply to the organization of the company.
The fourth line of defense, although not always formalized, is present in many companies as it involves external entities that will be in charge of audits.
The fifth line of defense is more specific to certain sectors such as banking. It consists of regulatory bodies such as the ACPR in France, FINMA in Switzerland, or BaFin in Germany.
The Three Lines of Defense Model is thus an essential tool to help companies adopt a structure and processes that are effective in reducing risks and achieving their objectives.
The use of internal control software and risk management software also supports this by efficiently simplifying their management.
